QMC6309
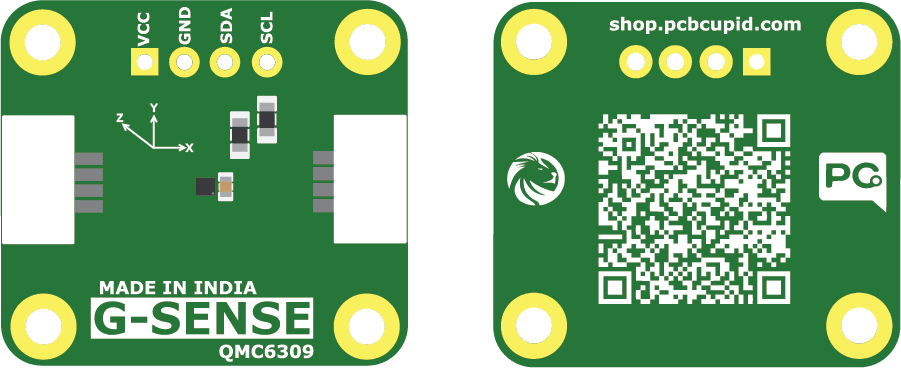
overview
The QMC6309, produced by QST Corporation, is a compact and energy-efficient digital magnetometer designed to detect magnetic fields across three axes (X, Y, Z). It integrates both magnetic sensing elements and signal-conditioning circuitry into a single silicon chip.
The QMC6309 stands out as a diminutive, energy-efficient, and accurate 3-axis magnetometer solution, ideal for compact and embedded electronics like VR trackers and flight controllers. With its seamless integration of sensing and signal conditioning, it provides high-precision magnetic field data with minimal PCB footprint.
Pin Configuration
- VCC - Power supply
- GND - Ground connection
- SDA - SDA of glyph board
- SCL - SCL of glyph board
Key Features
- 3-axis magnetic field sensing (X, Y, Z)
- I²C digital interface for easy MCU integration
- 16-bit ADC resolution for high-precision measurements
- Wide supply voltage range: 2.5 V – 3.6 V
- Low operating current: ~2 mA (ideal for battery-powered devices)
- Designed for consumer electronics like VR trackers, wearables, and flight controllers
Applications
- VR / AR Trackers – orientation tracking and drift correction
- Robotics & Drones – navigation, stabilization, and position control
- Consumer Electronics – smartwatches, handheld devices, portable gadgets
- Flight Controllers – magnetic heading reference in UAVs and quadcopters
- Research & Education – low-cost magnetometer for embedded learning projects
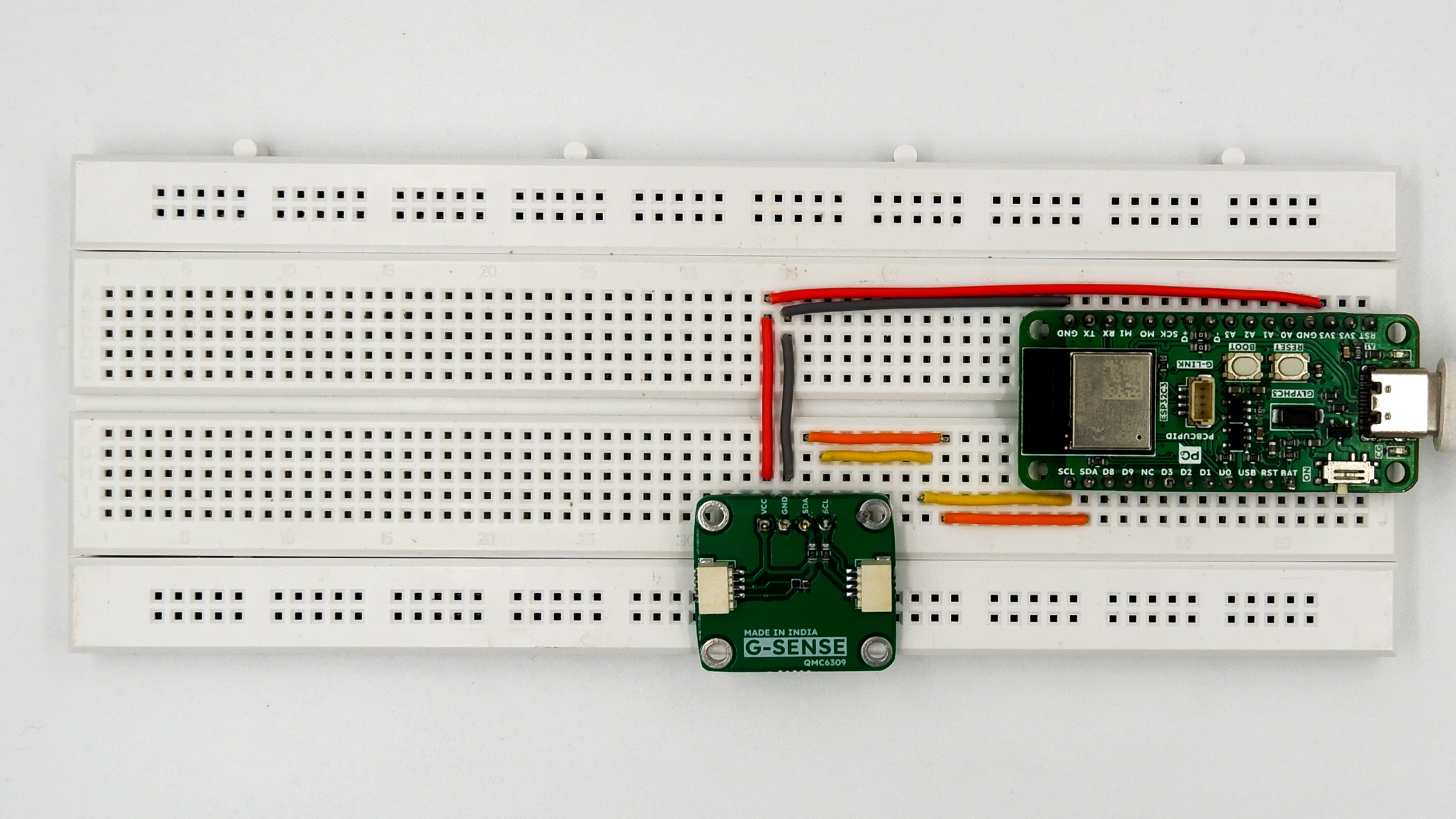
QMC6309 Simple Example
Step 1: Hardware Required
- Glyph Boards
- QMC6309
Step 2: Circuit Diagram
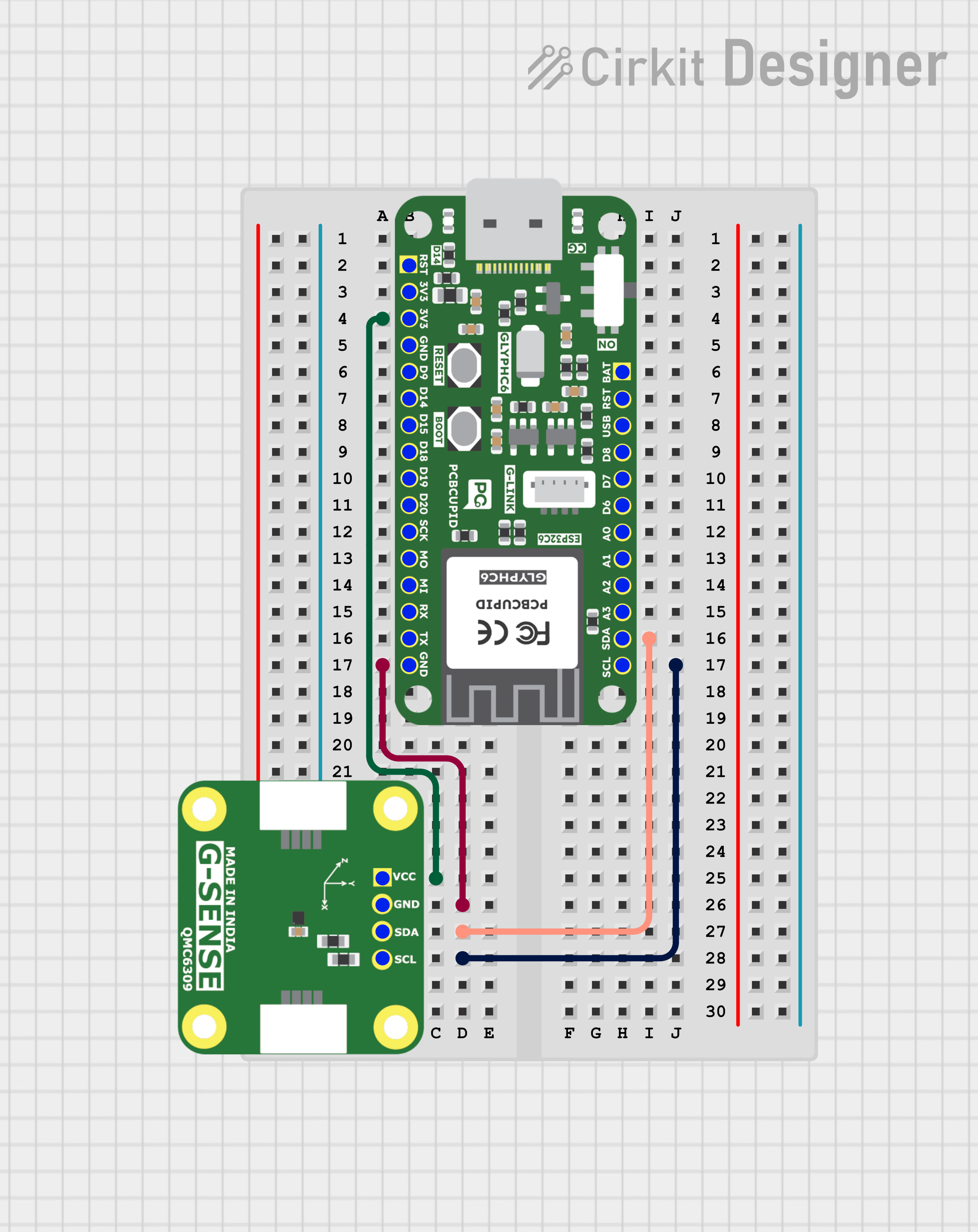
Step 3: Code Setup
- Open Arduino IDE.
- Make sure to install the library
- Copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE:
Step 4: Upload the Code
//You can download the PCBCUPID_QMC6309 library from here : https://github.com/pcbcupid/PCBCUPID-QMC6309
#include <Wire.h>
#include "PCBCUPID_QMC6309.h"
#include "ExponentialFilter.h"
PCBCUPID_QMC6309 mag(Wire);
// Calibrated offsets
const float x_offset = 3485.0;
const float y_offset = 1290.0;
const float declination = 0.22;
// Filter object: 0.2 weight (20%)
ExponentialFilter headingFilter(0.2, 0.0);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
if (!mag.begin()) {
Serial.println("Magnetometer init failed");
while (1);
}
Serial.println("Heading with Exponential Filter");
}
void loop() {
int16_t x, y, z;
if (mag.readRaw(x, y, z)) {
float x_cal = x - x_offset;
float y_cal = y - y_offset;
float heading = atan2(-x_cal, y_cal) + declination;
if (heading < 0) heading += 2 * PI;
if (heading > 2 * PI) heading -= 2 * PI;
float headingDeg = heading * 180.0 / PI;
// Apply exponential filter
headingFilter.update(headingDeg);
float smoothedHeading = headingFilter.get();
Serial.print("Heading: ");
Serial.print(smoothedHeading, 1);
Serial.print("° (");
Serial.print(mag.headingToDirection(smoothedHeading));
Serial.println(")");
}
delay(200);
}
- Connect the Board
- Connect your GLYPH board to your computer
- Select the Board and Port
Do the following settings in your Arduino IDE,
Tools > Board > esp32 > Pcbcupid GLYPH C3
For the Pcbcupid Glyph C3 to appear under Tools > Board > esp32, the esp32 board version installed in the Arduino IDE should be greater or equal to 3.1.0.
Tools > Portand select the port connected to your GLYPH.Tools > USB CDC on Boot >Enabled
If USB CDC on BOOT not enabled, you won't be seeing any serial data on Arduino IDE.
-
Upload the Code
- Click the upload button (➡️ icon) or use the shortcut
CRTL + Uin Arduino IDE to upload the code to the board.
- Click the upload button (➡️ icon) or use the shortcut
Step 5: Observe the Output
The output shows the smoothed compass heading in degrees (0–360°) along with its cardinal direction (e.g., N, NE, E, SE, etc.). Might not have accurate reading as this was not the intended purpose, This module is very useful to find strong magnetic field in 3 dimensional space.

QMC6309 with oled
Step 1: Hardware Required
- Glyph Boards
- QMC6309
- OLED Display
Step 2: Circuit Diagram
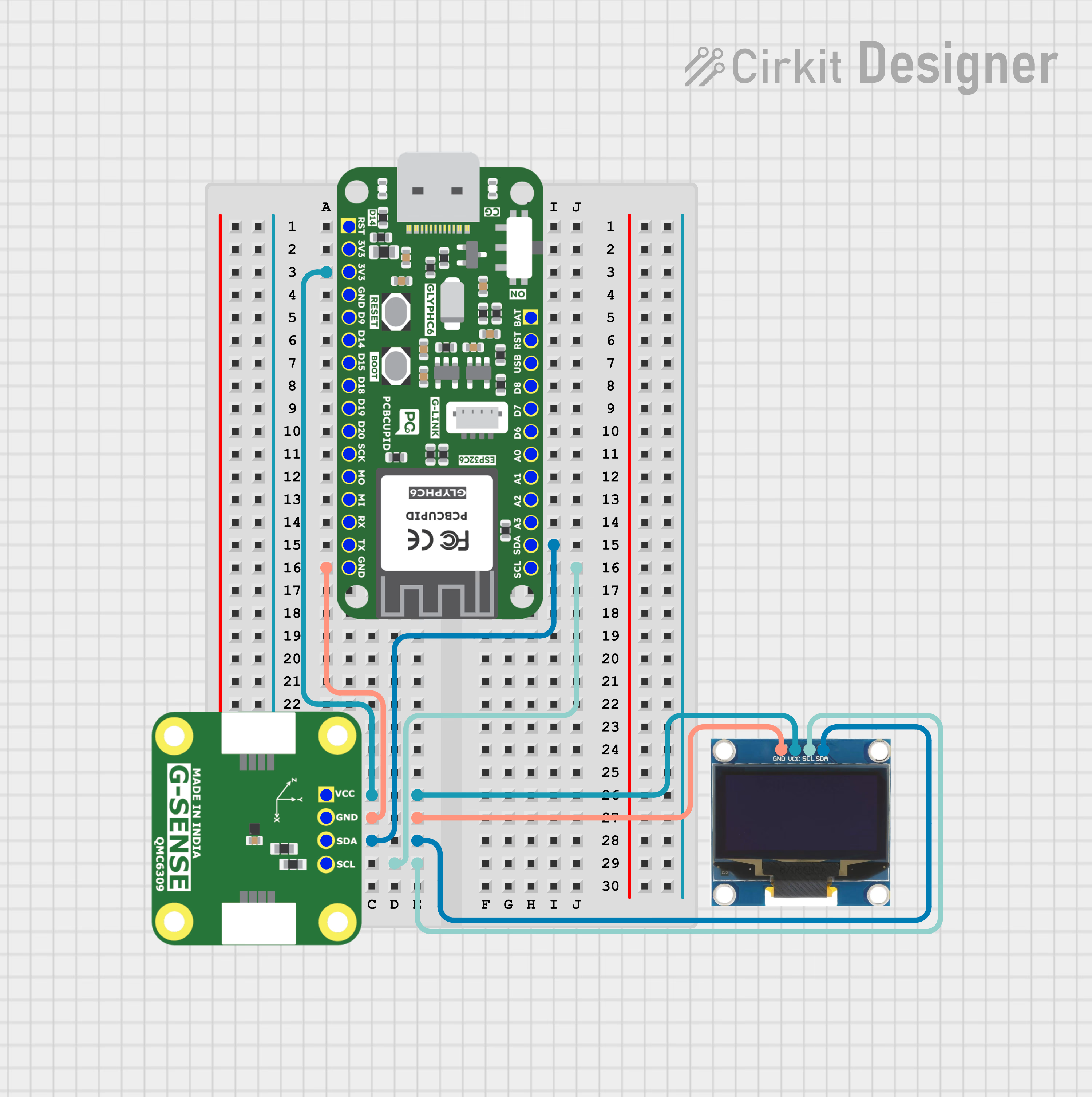
Step 3: Code Setup
- Open Arduino IDE.
- Make sure to install the "Audio Tool" library
- Copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE:
Step 4: Upload the Code
#include <Wire.h>
#include "PCBCUPID_QMC6309.h"
#include <U8g2lib.h>
// === OLED & Magnetometer ===
U8G2_SSD1306_128X64_NONAME_F_HW_I2C u8g2(U8G2_R0, U8X8_PIN_NONE);
PCBCUPID_QMC6309 mag(Wire);
// === Graph Box Settings ===
const int graphX = 70;
const int graphY = 8;
const int graphWidth = 54;
const int graphHeight = 48;
const int baselineY = graphY + graphHeight / 2;
const int barHeightMax = graphHeight / 2;
const int barWidth = 5;
const int barSpacing = 18;
const int barStartX = graphX + 9;
const int barRange = 500;
// === Baseline Calibration ===
long avgX = 0, avgY = 0, avgZ = 0;
int samples = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Wire.begin();
if (!mag.begin()) {
Serial.println("QMC6309 not found!");
while (1);
}
u8g2.begin();
}
void loop() {
int16_t x, y, z;
if (mag.readRaw(x, y, z)) {
samples++;
avgX = ((avgX * (samples - 1)) + x) / samples;
avgY = ((avgY * (samples - 1)) + y) / samples;
avgZ = ((avgZ * (samples - 1)) + z) / samples;
u8g2.clearBuffer();
// === Serial Debug ===
Serial.print("X: "); Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(" Y: "); Serial.print(y);
Serial.print(" Z: "); Serial.println(z);
// === Left Side Text ===
u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_5x8_tr);
u8g2.setCursor(4, 10); u8g2.print("X: "); u8g2.print(x);
u8g2.setCursor(4, 20); u8g2.print("Y: "); u8g2.print(y);
u8g2.setCursor(4, 30); u8g2.print("Z: "); u8g2.print(z);
// === G-SENSE Label Box (Left) ===
u8g2.setDrawColor(1);
u8g2.drawBox(2, 38, 52, 12); // G-SENSE Box
u8g2.setDrawColor(0);
u8g2.setCursor(8, 47); u8g2.print("G-SENSE");
u8g2.setDrawColor(1);
// === QMC6309 Label aligned to right end of box ===
u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_4x6_tr);
u8g2.setCursor(54 - u8g2.getStrWidth("QMC6309"), 59);
u8g2.print("QMC6309");
// === Graph Box ===
u8g2.drawFrame(graphX, graphY, graphWidth, graphHeight);
u8g2.drawHLine(graphX, baselineY, graphWidth); // Midline only
// === Draw Bars (without vertical axis lines) ===
drawBar(barStartX + barSpacing * 0, x - avgX, "X");
drawBar(barStartX + barSpacing * 1, y - avgY, "Y");
drawBar(barStartX + barSpacing * 2, z - avgZ, "Z");
u8g2.sendBuffer();
}
delay(150);
}
void drawBar(int xCenter, int16_t delta, const char* label) {
int percent = map(delta, -barRange, barRange, -100, 100);
percent = constrain(percent, -100, 100);
int barHeight = map(abs(percent), 0, 100, 0, barHeightMax);
int yStart = (percent >= 0) ? (baselineY - barHeight) : baselineY;
// Clip to graph box
if (yStart < graphY) {
barHeight -= (graphY - yStart);
yStart = graphY;
}
if (yStart + barHeight > graphY + graphHeight) {
barHeight = (graphY + graphHeight) - yStart;
}
// Draw the bar
u8g2.drawBox(xCenter - barWidth / 2, yStart, barWidth, barHeight);
// % text outside box
u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_4x6_tr);
int percentY = (percent >= 0) ? (graphY - 2) : (graphY + graphHeight + 8);
u8g2.setCursor(xCenter - 6, percentY);
u8g2.print(percent); u8g2.print("%");
// Axis label below bar
u8g2.setCursor(xCenter - 2, graphY + graphHeight + 16);
u8g2.print(label);
}
- Connect the Board
- Connect your GLYPH board to your computer
- Select the Board and Port
Do the following settings in your Arduino IDE,
Tools > Board > esp32 > Pcbcupid GLYPH C3
For the Pcbcupid Glyph C3 to appear under Tools > Board > esp32, the esp32 board version installed in the Arduino IDE should be greater or equal to 3.1.0.
Tools > Portand select the port connected to your GLYPH.Tools > USB CDC on Boot >Enabled
If USB CDC on BOOT not enabled, you won't be seeing any serial data on Arduino IDE.
-
Upload the Code
- Click the upload button (➡️ icon) or use the shortcut
CRTL + Uin Arduino IDE to upload the code to the board.
- Click the upload button (➡️ icon) or use the shortcut
Step 5: Observe the Output
outputs real-time X, Y, Z magnetometer readings as both serial text and dynamic bar graphs on an OLED, showing deviation from running average with percentage values.

